Computer Security

1. Privacy Risks in Data Collection and Storage
Two most common risks are data breach and cybersecurity threats.
For example, there are some possibilities that employees with access to
databases might misuse or leak data even though they compromise user privacy.
By the leak, hackers may target databases, cloud storage systems to access
sensitive user data.
Breaches can expose PII and sensitive data, leading to identity theft, fraud,
or blackmail. Sometimes, users may not fully understand what data is being collected,
why it’s being collected, and how it will be used when they put personal information
in a website. This can be a serious problem where organizations share data with
third parties without clear user consent.
 To prevent these cases, organizations make sure to secure the user data by
encrypting both data at rest and data in transit. It makes data unreadable
to unauthorized parties. Moreover it only allows authorized personnel to
have access to sensitive data. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) and role-based
access controls (RBAC) are common ways to secure access.
Sources:
https://gdpr.eu/
https://iapp.org/
https://owasp.org/
To prevent these cases, organizations make sure to secure the user data by
encrypting both data at rest and data in transit. It makes data unreadable
to unauthorized parties. Moreover it only allows authorized personnel to
have access to sensitive data. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) and role-based
access controls (RBAC) are common ways to secure access.
Sources:
https://gdpr.eu/
https://iapp.org/
https://owasp.org/

2. Misuse and Protection of Computing Resources
There are various threats such as loss of information, security breaches,
and legal liability. For example, unauthorized copying of files is a threat as
it may lead to loss of confidential information. An employee using his own laptop
for business purposes may inadvertently take confidential information home at night
or retain this information when he leaves the organization. Downloading unauthorized
software or using P2P programs may introduce malware into the organization, leading
to theft of information or loss of system availability.
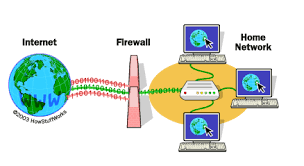
First way to protect a system from exploitation is using a firewall. A firewall
acts as a barrier between your internal network and the external internet, monitoring
and controlling incoming and outgoing traffic. It helps to filter out potentially
malicious connections and blocks unauthorized access to your network.
 The other way is using a strong password to safeguard your network against cyberattacks.
Hackers often take advantage of weak passwords to gain unauthorized access to systems
and obtain sensitive information. To maintain network security issues, enforcing password
complexity requirements- like using a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers,
special characters, and a minimum length- is crucial. In addition, regularly updating
passwords and avoiding the use of easily guessable information such as names or birth
dates can further enhance the strength of your passwords.
Sources:
https://avasant.com/
https://www.mcollins.com/protect-network-from-cyber-attacks/
The other way is using a strong password to safeguard your network against cyberattacks.
Hackers often take advantage of weak passwords to gain unauthorized access to systems
and obtain sensitive information. To maintain network security issues, enforcing password
complexity requirements- like using a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers,
special characters, and a minimum length- is crucial. In addition, regularly updating
passwords and avoiding the use of easily guessable information such as names or birth
dates can further enhance the strength of your passwords.
Sources:
https://avasant.com/
https://www.mcollins.com/protect-network-from-cyber-attacks/

3. Unauthorized Access to Information
Social engineering is used in almost all cyber attacks by hackers. It relies on manipulating
people into violating security procedures and divulging sensitive or personal information.
It is a very common technique used by hackers to gain unauthorized access. Social engineering
is highly effective because it gets over security controls by preying on human weaknesses and emotions.
For example, a common way is phishing. Hacker sends a message that appears to be legitimate,
with a malicious link or attachment. If the victim clicks the link, the hacker deploys malware
 and compromises their device. Depending on the type of malware, this may allow the hacker to
take over the user’s information.
To prevent this from happening, users could use strong passwords, use two-factor authentication,
avoid clicking on suspicious links or downloading unknown files, and regularly update your software
and stay informed about the latest security practices. Organizations can use robust security
measures such as strong access controls, data encryption, and regular security audits to prevent
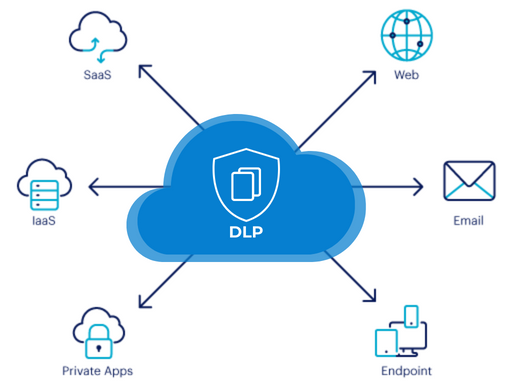
data leakage. Employee training on data handling best practices and the use of data loss prevention
(DLP) software can also prevent the risk of data breaches.
Source:
https://www.cynet.com/network-attacks/privilege-escalation/
https://www.teramind.co/
and compromises their device. Depending on the type of malware, this may allow the hacker to
take over the user’s information.
To prevent this from happening, users could use strong passwords, use two-factor authentication,
avoid clicking on suspicious links or downloading unknown files, and regularly update your software
and stay informed about the latest security practices. Organizations can use robust security
measures such as strong access controls, data encryption, and regular security audits to prevent
data leakage. Employee training on data handling best practices and the use of data loss prevention
(DLP) software can also prevent the risk of data breaches.
Source:
https://www.cynet.com/network-attacks/privilege-escalation/
https://www.teramind.co/

4. Benefits and Risks of Computing Innovations
One of the main benefits of computing innovation is that it increases efficiency and productivity.
For example, the automation of repetitive tasks through technologies like AI and machine learning
algorithms frees up valuable time for employees, allowing them to focus on more strategic and
creative tasks. This shift not only accelerates workflows but also reduces human error, leading
to more reliable outcomes and higher overall productivity.
Though computing innovation seems to have lots of avantages, it also has flaws. To begin, ethical
dilemmas such as job displacement is a huge problem. The advancement of AI automation has the
potential to replace human jobs, resulting in widespread unemployment and increasing economic
inequalities. There is a high possibility that AI will replace knowledge workers – like robots
are replacing manual laborers . AI has the potential to create far more jobs than it destroys.
 Addressing the impacts of job displacement requires proactive measures such as retraining programs
and policies that facilitate a just transition for affected workers, as well as far-reaching social
and economic support systems.
As technology develops, it often moves further beyond its original purpose. For example, social media
was initially created to help people connect but has led to increased mental health issues, such as
anxiety and depression, especially among younger generations. Furthermore, the internet aimed to
democratize knowledge but it has resulted in privacy violations, misinformation, and cybersecurity
threats. These various issues of technology are still affecting peoples in the world and are a serious
problem when considering technology advancement.
Sources:
https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/benefits-implementing-new-computer-technologies-z7nye
https://www.captechu.edu/blog/ethical-considerations-of-artificial-intelligence
Addressing the impacts of job displacement requires proactive measures such as retraining programs
and policies that facilitate a just transition for affected workers, as well as far-reaching social
and economic support systems.
As technology develops, it often moves further beyond its original purpose. For example, social media
was initially created to help people connect but has led to increased mental health issues, such as
anxiety and depression, especially among younger generations. Furthermore, the internet aimed to
democratize knowledge but it has resulted in privacy violations, misinformation, and cybersecurity
threats. These various issues of technology are still affecting peoples in the world and are a serious
problem when considering technology advancement.
Sources:
https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/benefits-implementing-new-computer-technologies-z7nye
https://www.captechu.edu/blog/ethical-considerations-of-artificial-intelligence

 To prevent these cases, organizations make sure to secure the user data by
encrypting both data at rest and data in transit. It makes data unreadable
to unauthorized parties. Moreover it only allows authorized personnel to
have access to sensitive data. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) and role-based
access controls (RBAC) are common ways to secure access.
Sources:
https://gdpr.eu/
https://iapp.org/
https://owasp.org/
To prevent these cases, organizations make sure to secure the user data by
encrypting both data at rest and data in transit. It makes data unreadable
to unauthorized parties. Moreover it only allows authorized personnel to
have access to sensitive data. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) and role-based
access controls (RBAC) are common ways to secure access.
Sources:
https://gdpr.eu/
https://iapp.org/
https://owasp.org/

 The other way is using a strong password to safeguard your network against cyberattacks.
Hackers often take advantage of weak passwords to gain unauthorized access to systems
and obtain sensitive information. To maintain network security issues, enforcing password
complexity requirements- like using a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers,
special characters, and a minimum length- is crucial. In addition, regularly updating
passwords and avoiding the use of easily guessable information such as names or birth
dates can further enhance the strength of your passwords.
Sources:
https://avasant.com/
https://www.mcollins.com/protect-network-from-cyber-attacks/
The other way is using a strong password to safeguard your network against cyberattacks.
Hackers often take advantage of weak passwords to gain unauthorized access to systems
and obtain sensitive information. To maintain network security issues, enforcing password
complexity requirements- like using a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers,
special characters, and a minimum length- is crucial. In addition, regularly updating
passwords and avoiding the use of easily guessable information such as names or birth
dates can further enhance the strength of your passwords.
Sources:
https://avasant.com/
https://www.mcollins.com/protect-network-from-cyber-attacks/

 and compromises their device. Depending on the type of malware, this may allow the hacker to
take over the user’s information.
To prevent this from happening, users could use strong passwords, use two-factor authentication,
avoid clicking on suspicious links or downloading unknown files, and regularly update your software
and stay informed about the latest security practices. Organizations can use robust security
measures such as strong access controls, data encryption, and regular security audits to prevent
data leakage. Employee training on data handling best practices and the use of data loss prevention
(DLP) software can also prevent the risk of data breaches.
Source:
https://www.cynet.com/network-attacks/privilege-escalation/
https://www.teramind.co/
and compromises their device. Depending on the type of malware, this may allow the hacker to
take over the user’s information.
To prevent this from happening, users could use strong passwords, use two-factor authentication,
avoid clicking on suspicious links or downloading unknown files, and regularly update your software
and stay informed about the latest security practices. Organizations can use robust security
measures such as strong access controls, data encryption, and regular security audits to prevent
data leakage. Employee training on data handling best practices and the use of data loss prevention
(DLP) software can also prevent the risk of data breaches.
Source:
https://www.cynet.com/network-attacks/privilege-escalation/
https://www.teramind.co/

 Addressing the impacts of job displacement requires proactive measures such as retraining programs
and policies that facilitate a just transition for affected workers, as well as far-reaching social
and economic support systems.
As technology develops, it often moves further beyond its original purpose. For example, social media
was initially created to help people connect but has led to increased mental health issues, such as
anxiety and depression, especially among younger generations. Furthermore, the internet aimed to
democratize knowledge but it has resulted in privacy violations, misinformation, and cybersecurity
threats. These various issues of technology are still affecting peoples in the world and are a serious
problem when considering technology advancement.
Sources:
https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/benefits-implementing-new-computer-technologies-z7nye
https://www.captechu.edu/blog/ethical-considerations-of-artificial-intelligence
Addressing the impacts of job displacement requires proactive measures such as retraining programs
and policies that facilitate a just transition for affected workers, as well as far-reaching social
and economic support systems.
As technology develops, it often moves further beyond its original purpose. For example, social media
was initially created to help people connect but has led to increased mental health issues, such as
anxiety and depression, especially among younger generations. Furthermore, the internet aimed to
democratize knowledge but it has resulted in privacy violations, misinformation, and cybersecurity
threats. These various issues of technology are still affecting peoples in the world and are a serious
problem when considering technology advancement.
Sources:
https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/benefits-implementing-new-computer-technologies-z7nye
https://www.captechu.edu/blog/ethical-considerations-of-artificial-intelligence